डाइमिथाइलमैग्नीशियम
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dimethylmagnesium
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H6Mg | |
| Molar mass | 54.375 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.96 g/cm3 |
| Reacts | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Dibutylmagnesium |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
डाइमिथाइलमैग्नीशियम एक ऑर्गेनोमैग्नीशियम यौगिक है। यह एक सफेद पायरोफोरिक ठोस है।[1][2] डाइमिथाइलमैग्नीशियम का उपयोग ऑर्गोनोमेटिक यौगिकों के संश्लेषण में किया जाता है।
तैयारी
अन्य डायलकाइलमैग्नीशियम यौगिकों की तरह, डाइमिथाइलमैग्नीशियम को मिथाइलमैग्नीशियम क्लोराइड के घोल में डाइअॉॉक्सिन मिलाकर तैयार किया जाता है:[3]: 2 सीएच3MgX + 2 डाइऑक्सेन ⇌ (सीएच3)2एमजी + एमजीएक्स2(μ-डाइअॉॉक्सेन)2↓ ऐसी प्रक्रियाओं में, डाइमिथाइलमैग्नीशियम ईथर के जोड़ के रूप में मौजूद होता है, बहुलक के रूप में नहीं।[4]
1,4-डाइअॉॉक्सेन के योग से ठोस MgX का अवक्षेपण होता है2(μ-डाइअॉॉक्सेन)2, एक समन्वय बहुलक ।[4] यह अवक्षेपण Schlenk संतुलन को (CH.) की ओर ले जाता है3)2मिलीग्राम। संबंधित विधियों को अन्य डायलकाइलमैग्नीशियम यौगिकों पर लागू किया गया है।[3] dimethylmercury और मैग्नीशियम को मिलाकर डाइमिथाइलमैग्नीशियम भी तैयार किया जा सकता है।[5][6]
गुण
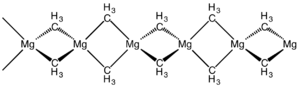
इस यौगिक की संरचना एक्स - रे क्रिस्टलोग्राफी द्वारा निर्धारित की गई है। सामग्री सिलिकॉन डाइसल्फ़ाइड के समान कनेक्टिविटी वाला एक बहुलक है, जिसमें टेट्राहेड्रल मैग्नीशियम केंद्र होते हैं, प्रत्येक मिथाइल समूहों को पाटने से घिरा होता है। Mg-C की दूरी दोपहर 224 बजे है।[7] डाइमिथाइलबेरिलियम समान संरचना को अपनाता है।[8]
संदर्भ
- ↑ Cope, A. C. (1935). "The Preparation of Dialkylmagnesium Compounds from Grignard Reagents". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 57 (11): 2238–2240. doi:10.1021/ja01314a059.
- ↑ Anteunis, M. (1962). "Studies of the Grignard Reaction. II. Kinetics of the Reaction of Dimethylmagnesium with Benzophenone and of Methylmagnesium Bromide-Magnesium Bromide with Pinacolone". J. Org. Chem. 27 (2): 596–598. doi:10.1021/jo01049a060.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Richard A. Andersen, Geoffrey Wilkinson (1979). "Bis[(Trimethylsilyl)Methyl] Magnesium". Inorg. Synth. 19: 262–265. doi:10.1002/9780470132500.ch61.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Fischer, Reinald; Görls, Helmar; Meisinger, Philippe R.; Suxdorf, Regina; Westerhausen, Matthias (2019). "Structure–Solubility Relationship of 1,4‐Dioxane Complexes of Di(hydrocarbyl)magnesium". Chemistry – A European Journal. 25 (55): 12830–12841. doi:10.1002/chem.201903120. PMC 7027550. PMID 31328293.
- ↑ Houben-Weyl Methods of Organic Chemistry Vol. XIII/2a, 4th Edition Organometallic Compounds of Group II of the Periodic Table (except mercury) (in German), Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, p. 215, ISBN 978-3-13-180654-3
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ↑ Jane E. Macintyre (1994), Dictionary of Organometallic Compounds (in German), CRC Press, p. 2273, ISBN 978-0-412-43060-2
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ↑ Weiss, E. (1964). "Die Kristallstruktur des Dimethylmagnesiums". J. Organomet. Chem. 2 (4): 314–321. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)82217-2.
- ↑ Snow, A.I.; Rundle, R.E. (1951). "Structure of Dimethylberyllium". Acta Crystallographica. 4 (4): 348–52. doi:10.1107/S0365110X51001100. hdl:2027/mdp.39015095081207.
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles with changed CASNo identifier
- Articles with changed ChemSpider identifier
- Articles with changed InChI identifier
- Pages using collapsible list with both background and text-align in titlestyle
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chembox image size set
- Templates that generate short descriptions
- ऑर्गनोमैग्नीशियम यौगिक
- Machine Translated Page
- Created On 06/01/2023